In 2017, the World Health Organization proposed the strategy of "early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment", which is intended to remind the public to pay attention to symptoms in advance. After years of clinical real money, these three strategies have become the most effective way to prevent cancer.
According to the "Global Cancer Report 2020" released by the WHO, it is predicted that the number of new cancers worldwide will increase to 30.2 million in 2040 and the number of deaths will reach 16.3 million.
In 2020, there will be 19 million new cancers in the world. At that time, the three major cancers with the largest number of cancers in the world are: breast cancer (22.61 million), lung cancer (2.206 million), colon (19.31 million), and gastric cancer ranked fifth with 10.89 million , in the number of new cancers, colon cancer and gastric cancer accounted for 15.8% of all new cancers.

As we all know, the Manhua tract refers to from the mouth to the rainbow door, which involves the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (cecum, appendix, colon, rectum and anal canal), liver, pancreas, etc., and the colorectum in new cancers worldwide Cancer and gastric cancer both belong to the digestive tract, so digestive tract-related cancers also need to be paid attention to and the "three early" strategy should be implemented.
In 2020, the number of new cancer cases in my country also reached 4.5 million, and the number of cancer deaths was 3 million. An average of 15,000 people were diagnosed with cancer every day, and 10.4 people were diagnosed with cancer every minute. The fifth is lung cancer (accounting for 17.9% of all new cancers), colorectal cancer (12.2%), gastric cancer (10.5%), breast cancer (9.1%), and liver cancer (9%). Among the top five cancers alone, gastrointestinal cancers accounted for 31.7% of all new cancers. It can be seen that we need to pay more attention to the detection and prevention of digestive tract cancer.
The following is the 2020 edition (special investigation and prevention recommendation of people's Chang Beihui tumor) involving digestive tract pain prevention and inspection plan:
Colorectal cancer
1.Asymptomatic people over 1.45 years old;
2.People over 240 with anorectal symptoms for two weeks":
3.Patients with ulcerative colitis for a long time;
4.4 people after colorectal cancer surgery;
5. The population after treatment of colorectal adenoma;
6. Immediate relatives with a family history of colorectal cancer
7. Immediate relatives of patients diagnosed with hereditary colorectal cancer who are over 20 years old
1. "General Population" Screening Meets 1-5:
(1) Colorectal cancer screening starts at the age of 45, regardless of male or female, fecal occult blood (FOBT) is detected once a year
Colonoscopy every 10 years until age 75;
(2) Those aged 76-85, who are in good health, and those with a life expectancy of more than 10 years, can continue to maintain the decoration.
2 In line with the "Clinical investigation of immediate family members with a family history of colorectal cancer:
(1) 1 first-degree relative with definite high-grade adenoma or pain (age of onset is less than 60 years old), 2
First-degree relatives and above with definite high-grade adenoma or cancer (any age of onset), starting at the age of 40 (or starting at 10 years younger than the age of onset of the youngest family member), FOBT examination once a year, once every 5 years Colonoscopy;
(2) High-risk subjects with a family history of first-degree relatives (only 1, and the age of onset is higher than 60 years old):
Start checking at the age of 40, with a FOBT test every year and a colonoscopy every ten years. 3 Screening of family members of "hereditary colorectal cancer" meeting 7;
For family members of patients with FAP and HNPCC, gene mutation testing is recommended when the gene mutation in the first case in the family is clear.
(1) For those with positive gene mutation test, after the age of 20, a colonoscopy should be performed every 1-2 years; (2) For those with a negative gene mutation test, the general population should be examined. 4 Recommended methods for checking:
(1) FOBT testing + inter-volume investigation is the main method of the Han investigation, and the evidence is sufficient:
(2) Multi-target gene detection of blood may help to improve the accuracy of the calculation, and the price is relatively expensive; (3) If conditions permit, screening can be carried out by combining stool and blood methods.
1. Exercise can effectively reduce the occurrence of tumors, adhere to sports leadership, and swim to avoid obesity;
2. Healthy brain food, increase the intake of crude fiber and fresh fruits, and avoid high-fat and high-protein diets;
3 Non-body anti-inflammatory and anticancer drugs may be effective in preventing bowel cancer. The elderly may try low-dose aspirin, which may reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and bowel cancer. Consult a doctor for specific use.
5.Reduce smoking to avoid its long-term toxicity and inflammatory stimulation to Qinghua Dao.
Stomach Cancer
Anyone who has one of the following conditions is a high-risk object;
1. Over 60 years old;
2 Moderate and severe atrophic gastritis;
3. Chronic gastric ulcer;
4. Stomach polyps;
5. Giant fold sign of gastric mucosa;
6. Postoperative residual stomach for benign diseases;
7. Remnant stomach after gastric cancer surgery (6-12 months after surgery);
8. Helicobacter pylori infection;
9. A clear family history of gastric or esophageal cancer;
10. Pernicious anemia:
11. Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) family history.

Age >40 years old with abdominal pain, abdominal distension, acid regurgitation, heartburn and other symptoms of epigastric discomfort, and chronic gastritis, gastric mucosal intestinal metaplasia, gastric polyps, remnant stomach, giant gastric fold sign, chronic gastric ulcer and gastric epithelial atypia Hyperplasia and other lesions and objects with a family history of tumors should undergo regular gastroscopy according to physician recommendations.
1. Establish healthy eating habits and diet structure, not overeating;
2. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection;
3. Reduce the consumption of cold, spicy, overheated, and hard foods, as well as high-salt foods such as smoked and pickled
4. Quit smoking;
5. Drink less or no hard alcohol;
6. Relax and decompress reasonably
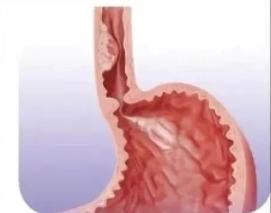
Esophageal cancer
Age > 40 years old and meet any of the following risk factors:
1. From the high-incidence area of esophageal cancer in my country (the most dense area of esophageal cancer in my country is located in Hebei, Henan and Shanxi provinces in the south of Taihang Mountain, especially in Cixian County, in Qinling, Dabie Mountain, northern Sichuan, Fujian, Guangdong, northern Jiangsu, Xinjiang, etc. land and organic pairs are concentrated in high-incidence areas);
2. Upper gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, acid regurgitation, eating discomfort and other symptoms;
3. Family history of esophageal pain:
4. Suffering from esophageal precancerous disease or precancerous lesions:
5. Have high risk factors for esophageal cancer such as smoking, heavy drinking, overweight, fond of hot food, squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck or respiratory tract;
6. Suffering from periesophageal reflux disease (CERD);
7. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
People at high risk of esophageal cancer:
1. Ordinary endoscopy, once every two years;
2 Endoscopy with pathological findings of mild dysplasia, endoscopy once a year;
3 Endoscopy with pathological findings of moderate dysplasia, endoscopy every six months
1. Do not smoke or quit smoking;
2. A small amount of alcohol or no alcohol;
3. Eat a reasonable diet, eat more fresh fruits and vegetables
4. Enhance exercise and maintain a healthy weight;
5. Do not eat hot food or drink hot water.
Liver cancer
Men over the age of 35 and women over the age of 45 in any of the following groups:
1. Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection or chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection;
2. Those with a family history of liver cancer;
3. Patients with liver cirrhosis caused by schistosomiasis, alcohol, primary biliary cirrhosis, etc.;
4. Patients with drug-induced liver damage;
5. Patients with inherited metabolic diseases, including: hemochromatosis a-1 antitrypsin deficiency, glycogen storage disease, delayed cutaneous porphyria, tyrosinemia, etc.;
6. Patients with autoimmune hepatitis;
7. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients
1. Men over 35 years old and women over 45 years old with high risk of liver cancer should be investigated;
2. Combined application of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and liver B-ultrasound, screening every 6 months
1. Hepatitis B vaccine;
2. Patients with chronic hepatitis should receive antiviral therapy as soon as possible to control the replication of hepatitis virus
3. Abstain from or reduce alcohol consumption;
4. Eat a light diet and reduce the intake of greasy food
5. Avoid the intake of moldy food.

Pancreatic cancer
People over the age of 40, especially over the age of 50, with any one of the following factors (the sixth item does not increase the risk of pancreatic cancer, but screening is generally not performed):
1. Family history of pancreatic cancer and diabetes;
2. There is a history of long-term smoking, drinking, high-fat and high-protein diet;
3. Middle and upper abdominal fullness, discomfort, abdominal pain without obvious cause, and symptoms such as loss of appetite, fatigue, diarrhea, weight loss, low back pain, etc.;
4. Repeated episodes of chronic pancreatitis, especially chronic pancreatitis with pancreatic duct stones, main pancreatic duct-type mucinous papilloma, mucinous cystic adenoma, and solid pseudopapillary tumor, with elevated serum CA19-9;
5. Recent sudden onset of diabetes mellitus without family history;
6. Helicobacter pylori (HP) positive, history of oral periodontitis, P-J syndrome, etc.
1. The above-mentioned subjects are screened with the results of blood tests of tumor markers such as CA19-9, CA125 CEA, etc., combined with abdominal CT and MRI, and B-ultrasound can also provide corresponding help;
2. CT or MR examination once a year for the above-mentioned population, especially those with family history and existing pancreatic lesions
1. Quit smoking and alcohol control;
2. Promote a light, easily digestible, low-fat diet;
3. Eat more poultry, fish and shrimp, and promote the consumption of "+" flower vegetables, such as green cabbage, cabbage, radish, broccoli, etc.;
4. Promote outdoor aerobic activities
5. In order to prevent the deterioration of benign lesions, those with pancreatic duct stones, intraductal mucinous papilloma and cystic adenoma or other benign pancreatic lesions should seek medical attention in time.
We, Jiangxi Zhuoruihua Medical Instrument Co.,Ltd., is a manufacturer in China specializing in the endoscopic consumables, such as biopsy forceps, hemoclip, polyp snare, sclerotherapy needle, spray catheter, cytology brushes, guidewire, stone retrieval basket, nasal biliary drainage catheter etc. which are widely used in EMR, ESD, ERCP. Our products are CE certified, and our plants are ISO certified. Our goods have been exported to Europe, North America, Middle East and part of Asia, and widely obtains the customer of the recognition and praise!
Post time: Sep-09-2022


