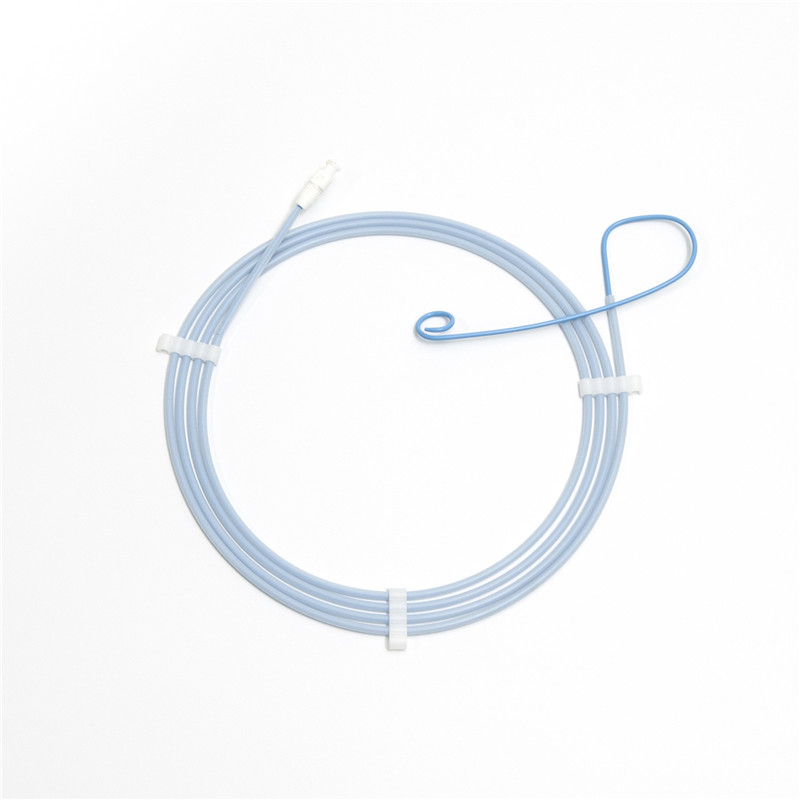
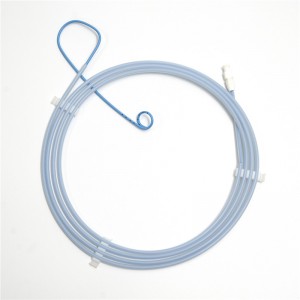
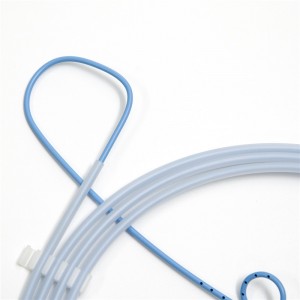
Medical Instrument Disposable Nasal Biliary Drainage Catheter for Ercp Operation
Medical Instrument Disposable Nasal Biliary Drainage Catheter for Ercp Operation
Application
Nasal Biliary Drainage Catheter is avaible through the mouth and nose and into the bile duct, mainly used for drainage of bile. It's disposable product.
Specification
| Model | O.D.(mm) | Length (mm) | Head End Type | Application Area |
| ZRH-PTN-A-7/17 | 2.3 (7FR) | 1700 | Left a | Liver duct |
| ZRH-PTN-A-7/26 | 2.3 (7FR) | 2600 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-A-8/17 | 2.7 (8FR) | 1700 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-A-8/26 | 2.7 (8FR) | 2600 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-B-7/17 | 2.3 (7FR) | 1700 | Right a | |
| ZRH-PTN-B-7/26 | 2.3 (7FR) | 2600 | Right a | |
| ZRH-PTN-B-8/17 | 2.7 (8FR) | 1700 | Right a | |
| ZRH-PTN-B-8/26 | 2.7 (8FR) | 2600 | Right a | |
| ZRH-PTN-D-7/17 | 2.3 (7FR) | 1700 | Pigtail a | Bile Duct |
| ZRH-PTN-D-7/26 | 2.3 (7FR) | 2600 | Pigtail a | |
| ZRH-PTN-D-8/17 | 2.7 (8FR) | 1700 | Pigtail a | |
| ZRH-PTN-D-8/26 | 2.7 (8FR) | 2600 | Pigtail a | |
| ZRH-PTN-A-7/17 | 2.3 (7FR) | 1700 | Left a | Liver duct |
| ZRH-PTN-A-7/26 | 2.3 (7FR) | 2600 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-A-8/17 | 2.7 (8FR) | 1700 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-A-8/26 | 2.7 (8FR) | 2600 | Left a | |
| ZRH-PTN-B-7/17 | 2.3 (7FR) | 1700 | Right a |
Products Description
Good resistance to folding and deformation,
easy to operate.
The round design of tip avoid the risks of scratch of tissues while passing through endoscope.
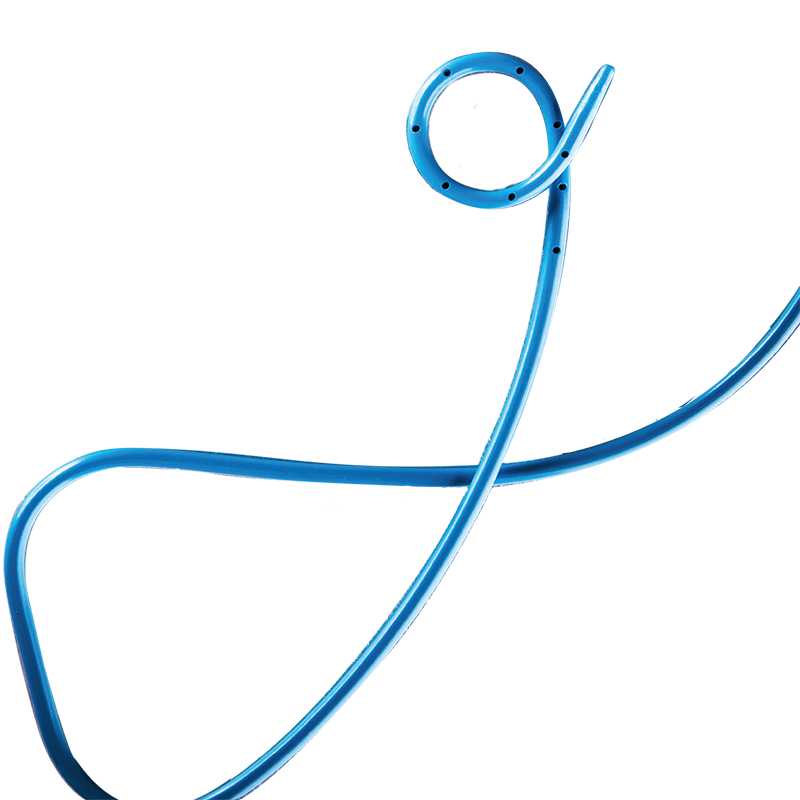
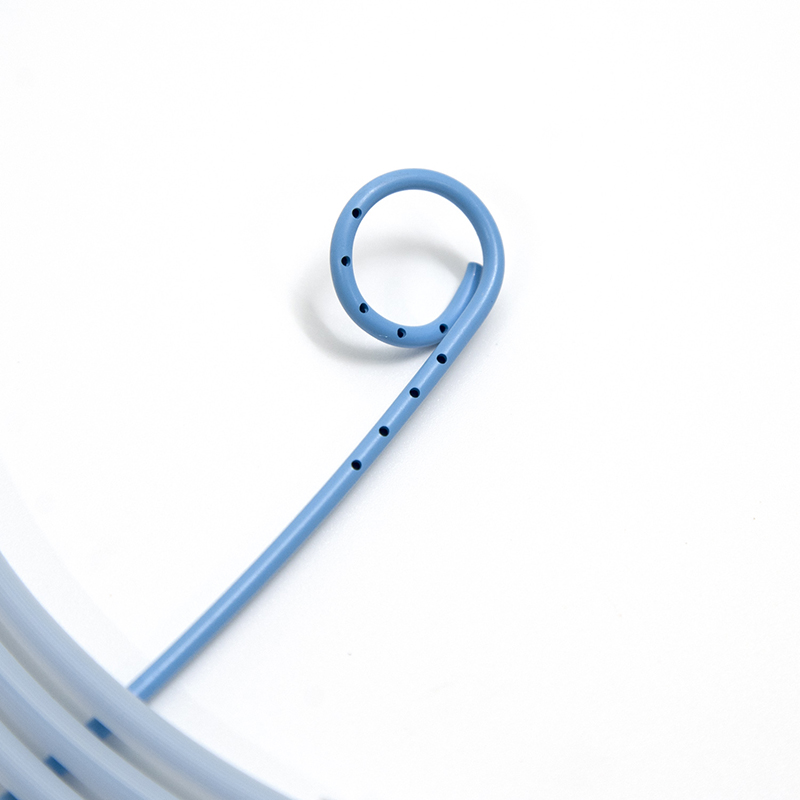


Multi-side hole, large internal cavity, good drainage effect.
The surface of the tube is smooth, moderate soft and hard, reducing patient pain and foreign body sensation.
Excellent plasticity at the end of the class, avoiding slippage.
Accept length customized.
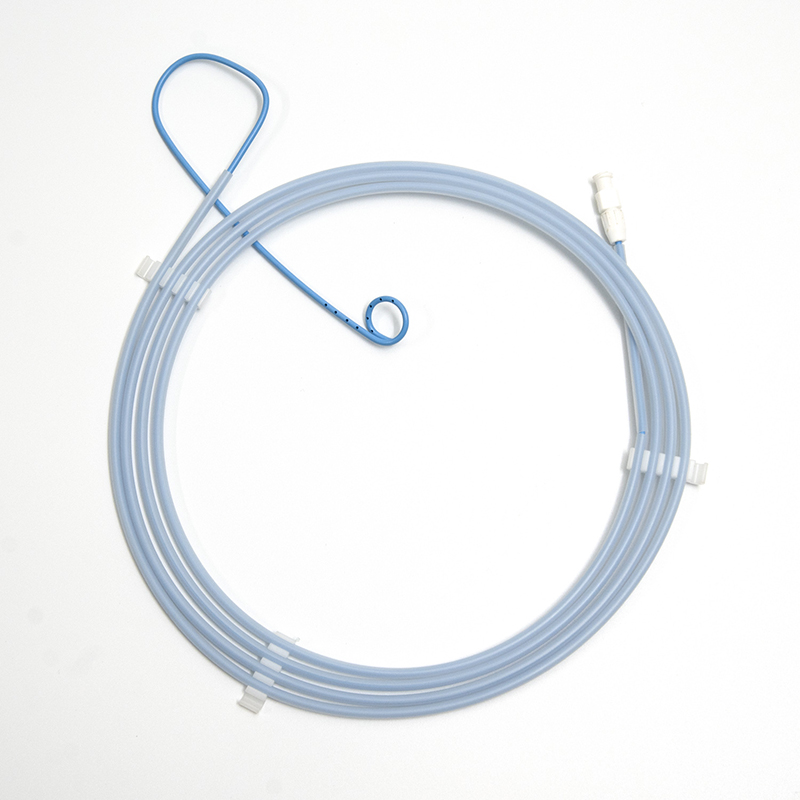

Endoscopic Nasobiliary Drainage is indicated for
1. Acute suppurative obstructive cholangitis;
2. Prevention of stone incarceration and bile duct infection after ERCP or lithotripsy;
3. Bile duct obstruction caused by primary or metastatic benign or malignant tumors;
4. Bile duct obstruction caused by hepatolithiasis;
5. Acute biliary pancreatitis;
6. Traumatic or iatrogenic bile duct stricture or biliary fistula;
7. The clinical need to repeat cholangiography or collect bile for biochemical and bacteriological examination;
8. Bile duct stones should be treated with drug litholysis;